Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a complex and chronic condition affecting millions of children, often persisting into adulthood. This comprehensive guide explores the symptoms, subtypes, and crucial information for understanding and managing ADHD.
Introduction: Understanding ADHD
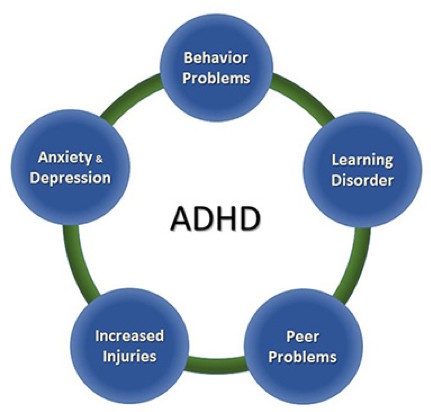
ADHD encompasses a combination of persistent challenges, including difficulty sustaining attention, hyperactivity, and impulsive behavior. Individuals with ADHD may face issues like low self-esteem, relationship difficulties, and academic underperformance. While symptoms may improve with age, some individuals continue to experience them into adulthood, requiring effective strategies for success.
Products & Services: A Practical Guide for Thriving
Our commitment to supporting individuals with ADHD extends to our comprehensive guide, “A Practical Guide to Help Kids of All Ages Thrive.” This resource provides valuable insights and strategies to empower those affected by ADHD, fostering personal and academic growth.
Symptoms of ADHD: Inattention and Hyperactivity-Impulsivity
ADHD symptoms manifest primarily as inattention and hyperactive-impulsive behavior. These symptoms typically emerge before the age of 12, with noticeable signs as early as 3 years old. Symptoms may vary in intensity, and their impact can extend into adulthood.
Subtypes of ADHD:
- Predominantly Inattentive:
- Difficulty focusing on details
- Trouble staying engaged in tasks
- Challenges following instructions
- Predominantly Hyperactive/Impulsive:
- Restlessness or constant motion
- Impulsivity in actions and speech
- Difficulty waiting for turn
- Combined:
- A mix of inattentive and hyperactive/impulsive symptoms
Inattention: Recognizing the Signs
Children displaying inattention patterns may exhibit:
- Careless mistakes in schoolwork
- Difficulty staying focused
- Lack of responsiveness when spoken to directly
- Trouble organizing tasks and activities
Hyperactivity and Impulsivity: Identifying the Traits
Children with hyperactivity and impulsivity may demonstrate:
- Restlessness or constant fidgeting
- Inability to stay seated
- Excessive talking and impulsiveness
- Difficulty waiting for their turn
Differentiating ADHD from Typical Behavior
Distinguishing typical behavior from ADHD symptoms is crucial. While short attention spans and high energy levels are common in children, persistent patterns warrant attention. ADHD should not be diagnosed solely based on differences in behavior compared to peers.
When to Seek Professional Help
If concerned about potential ADHD signs, consult a pediatrician or family doctor. A thorough medical evaluation, including referrals to specialists if necessary, helps rule out other causes. Early diagnosis and intervention significantly impact outcomes.
Conclusion: Empowering Lives Through Understanding
Understanding ADHD symptoms is a crucial step in effective management. At Brimex Medical, Inc., our commitment goes beyond awareness – we offer comprehensive intellectual and developmental disability support, empowering individuals to find their rightful place in the community. By combining our expertise with valuable resources, we aim to make a positive impact on the lives of those affected by ADHD.